Climate change influences the hydrological cycle with direct effects on water resources, such as lakes or groundwaters, which represent two of the most important supply sources for human consumption and irrigation.
Potential decrease of groundwater resources – due to both the increase of the demand and climate change – is of critical importance for water authorities since they are the main potable water supply source for human consumption and irrigation. Moreover, since the energy cost due to pumping stations is one of the most important components of the total system management costs, the analysis of the water table behavior has also very important economical implications.
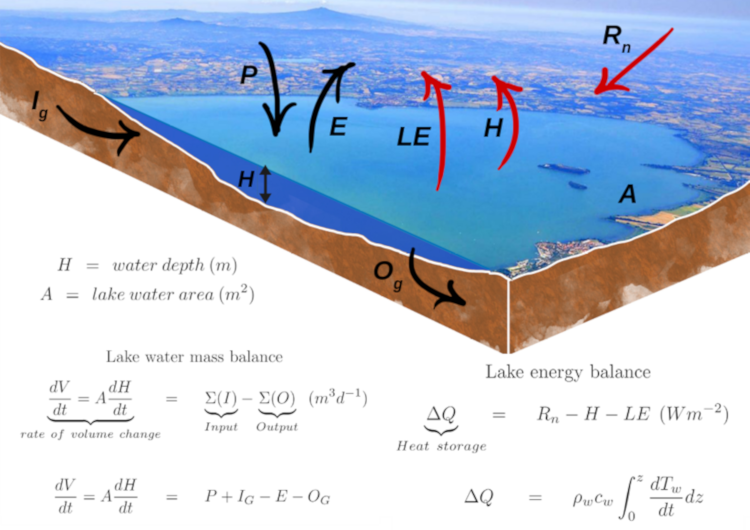
In the framework of assessing water balance and the related hydraulic works for water supply, the water resources section of CRC correlates quantitatively climate trends, precipitation, groundwater and lakes behaviour.